使用python刷网课时长
每年小学教师差不多要刷完2-3个平台的继续教育网课,每个平台的网课大概是30学时。大众平台的网课还好,可以使用Tampermonkey插件,在greasyfork社区里有很多可用来刷网课的脚本。小众平台的网课就要自己想办法了,虽然没有公用的脚本,但是有的可以倍速播放刷网课,或者可以无人值守挂着,那些都比较轻松。不过,现在的网课基本都有防挂机的检测,能挂机刷课的良心平台不多了。
今年就碰到了一个小众的平台,30学时的课程,有2个号需要刷网课。只能挂着每门课一点一点累计学习时间。更过分的是,还有防检测的机制,几分钟不动鼠标键盘或者学习时间长了就会弹出窗口验证一下——“在吗?”。这还怎么让我好好学习呢!那就分析一下怎么绕过检测或者其他简单点的刷课方法吧。
网课的地址是:
https://cn202334007.stu.teacher.com.cn/
分析网课计时规则
首先看一下这个平台的网课的页面构成,主要有2类页面,一类是总学习计划页面,一类是每门课的学习页面,总共有15门课,因此共有15个学习页面。
在总学习计划页面可以看到每门课的学习情况,并且能够点进各门课去学习。当每门课学习完成后显示“已完成”并获得2学时,因此15门课程都需要完成。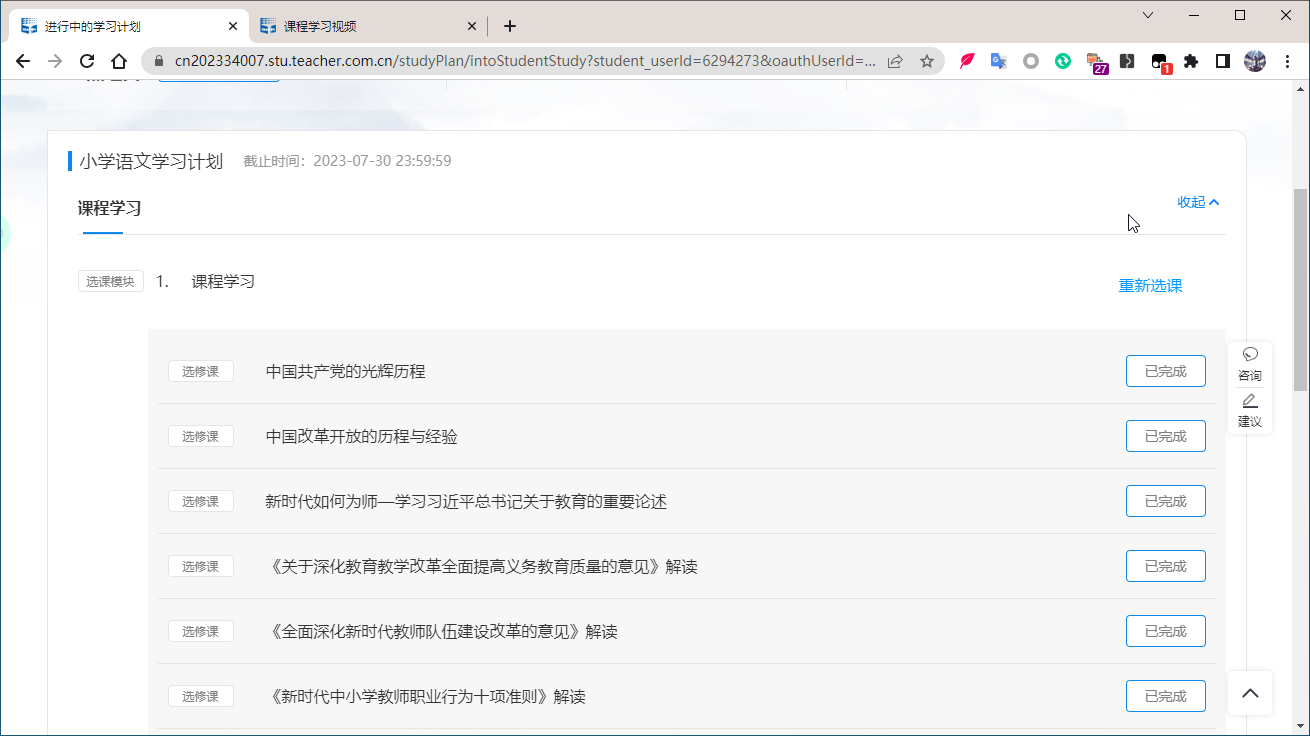
在其中一个课程的学习页面中可以看到右下角有统计学习情况的信息——“本课程学时数:2.0 最长可累计时间:90分钟(1学时=45分钟) 本课程已学习时间:0分钟”。因此,需要“本课程已学习时间:90分钟”才算完成。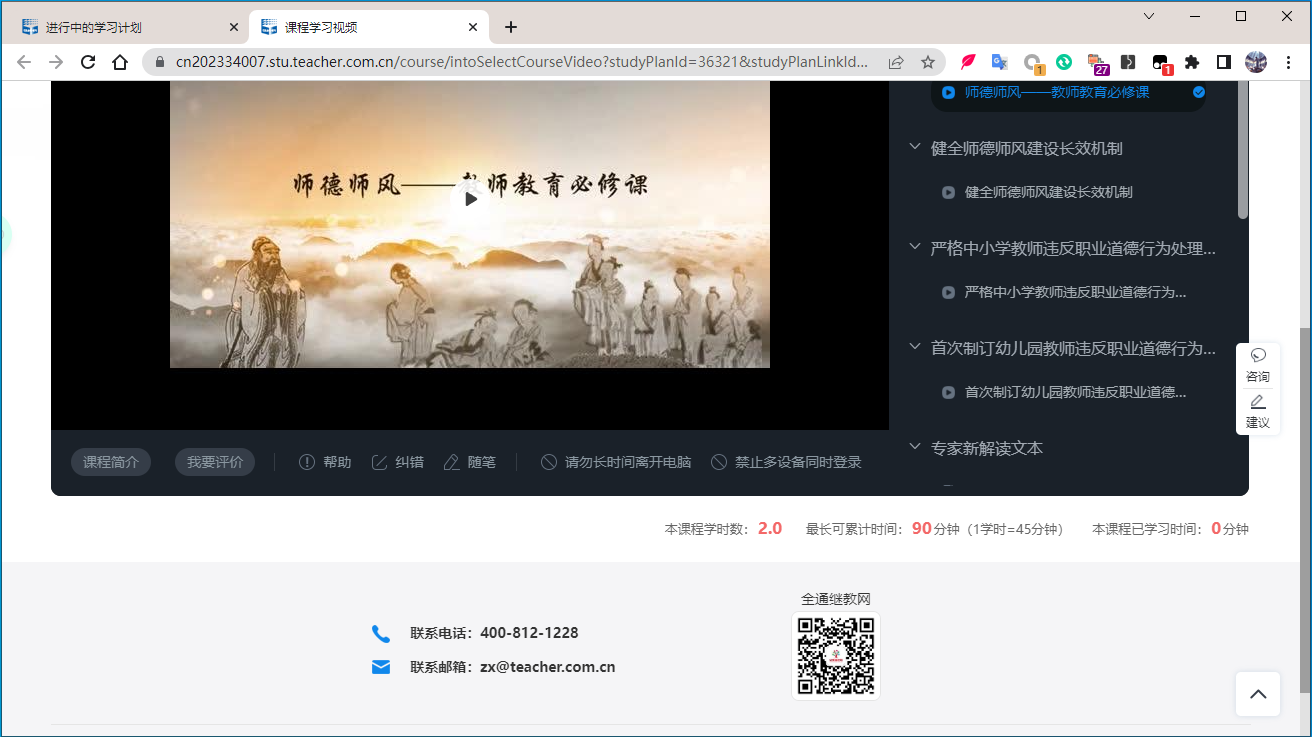
在首次刷课时,倍速看完了所有的视频,只花了10几分钟,但是学习时间并没有倍速,因此我怀疑是浏览器的时间影响着学习时间。找到了“TimerHooker”脚本可以加速整个浏览器当前页面时间,经测试脚本生效,但是还是没有倍速“本课程已学习时间”。
前端源码DEBUG
接着看一下网页的源码,按F12DEBUG看看。找到Sources选项卡的index.js文件。看到有courseStudyTime这个变量,从命名来看,大概率跟需要累计的学习时间相关。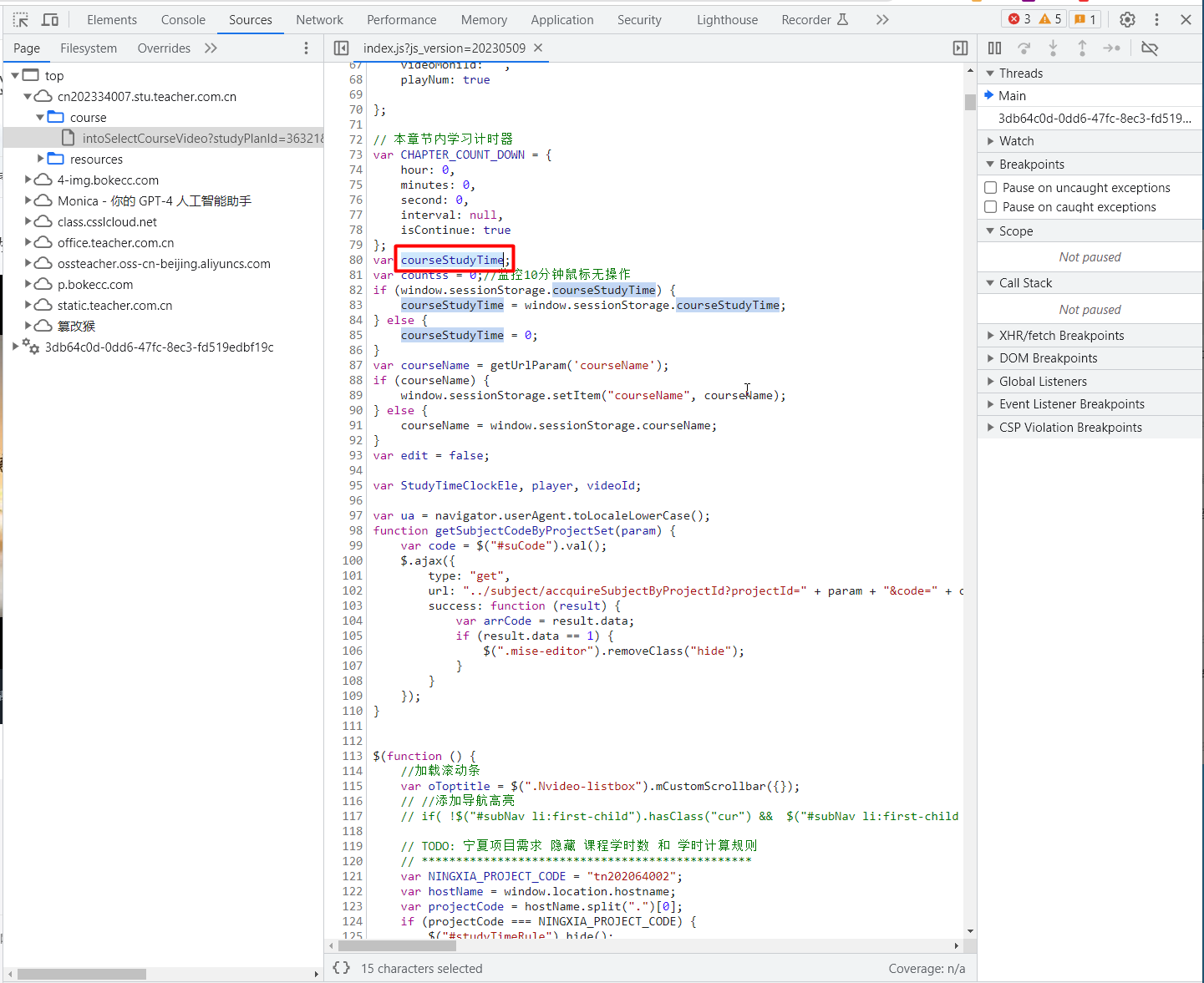
快速浏览一下,在代码的第2161行处有一个startTimeClock()函数,courseStudyTime以每秒的速度加1,很符合实际情况中累计的学习时间,且单位为秒(s)。那么修改加大courseStudyTime值的增速呢,是不是能够倍速“本课程已学习时间”。
修改前代码:
//学习时长开始计时
function startTimeClock() {
StudyTimeClockEle = setInterval(function () {
courseStudyTime++;
window.sessionStorage.setItem("courseStudyTime", courseStudyTime);
}, 1000);
}修改后代码:
//学习时长开始计时
function startTimeClock() {
StudyTimeClockEle = setInterval(function () {
courseStudyTime++;
courseStudyTime++; //多加几次
window.sessionStorage.setItem("courseStudyTime", courseStudyTime);
}, 100); //由1000ms累加一次,改为100ms累加一次
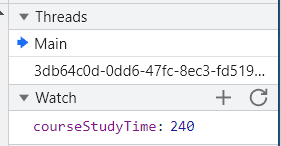
}修改后Watch一下courseStudyTime值,经测试courseStudyTime确实加速增大了。但是,“本课程已学习时间”并没有加快。
接着分析原因,在2237行处的代码isGetStudyRecordStorage()函数中,由变量obj中的成员"studyTime": Math.round(courseStudyTime / 60)和ajax中包含的type: 'post',data: JSON.stringify(obj)基本可以推测Browser端发送一个Post包给Server端,且是以字段studyTime分钟为单位的形式累加学习时长。
function isGetStudyRecordStorage(result, type) {
var getStartTime = result.data.courstTime.startTime.replace(/-/g, "/");
var getEndTime = result.data.courstTime.endTime.replace(/-/g, "/");
var start = getStartTime.replace(/-/g, "/");
var end = getEndTime.replace(/-/g, "/");
var endTime = new Date(end).getTime();
var startTime = new Date(start).getTime();
var nowTime = getCurrentDate();
var period = result.data.courstTime.studyHour;//获取课程学时
$('.addCourseTime').attr('data-period', period);
if (nowTime - startTime > 0 && nowTime - endTime < 0) {
// var studyTime = type ? 0 : Math.round(courseStudyTime / 60);
var obj = {
"studyCircleId": studyCircleId,
"userId": userId,
"subjectTableId": subjectTableId,
"fatherTableId": courseCataId,
"studyType": mediumType,
"studyTime": Math.round(courseStudyTime / 60),
"action": "学习",
"deviceType": "pc端",
"studyPlanId": studyPlanId,
"courseCode": courseCode,
"period": period,
"courseTypeAndId":fid,
"flagCode": "20200617"
}
if (mediumType == 1) {
if(player && player.getPosition && $("video").length>0){
obj.videoTime = player.getPosition();
}else{
obj.videoTime = null;
}
//obj.videoTime = player ? player.getPosition() : null; //获取视频时长
}
if (type == "hand") {
obj.actionType = "hand";
} else {
obj.actionType = type ? 'self' : 'auto';
}
$.ajax({
url: '../studyRecord/insertStudyRecord',
type: 'post',
contentType: 'application/json',
data: JSON.stringify(obj),
dataType: "json",
success: function (result) {
setTimeout(function () {
getStudyTime(period)
},2000);
if (result.isSuccess == 1) {
courseStudyTime = 0;
window.sessionStorage.courseStudyTime = 0;
//判断课程是否学习过
isStudySections();
}else if(result.isSuccess == 1001){
window.location.href = encodeURI('../studyRecord/soldoutcourse?message='+result.msg);
}
}
});
}else{ //已结束
setTimeout(function () {
getStudyTime(period)
},2000);
$(".studyTime").css("display","none");
$(".studyCourseTimeRefresh").css("display","none");
}
}接着打开Network选项卡,点击网页中“刷新学习时间”后可以看到Broswer端有4个数据包的发送给Server端。分别为:
- getThisTime
- insertStudyRecord
- getCourseWhetherWatch
- findCourseStudyTime
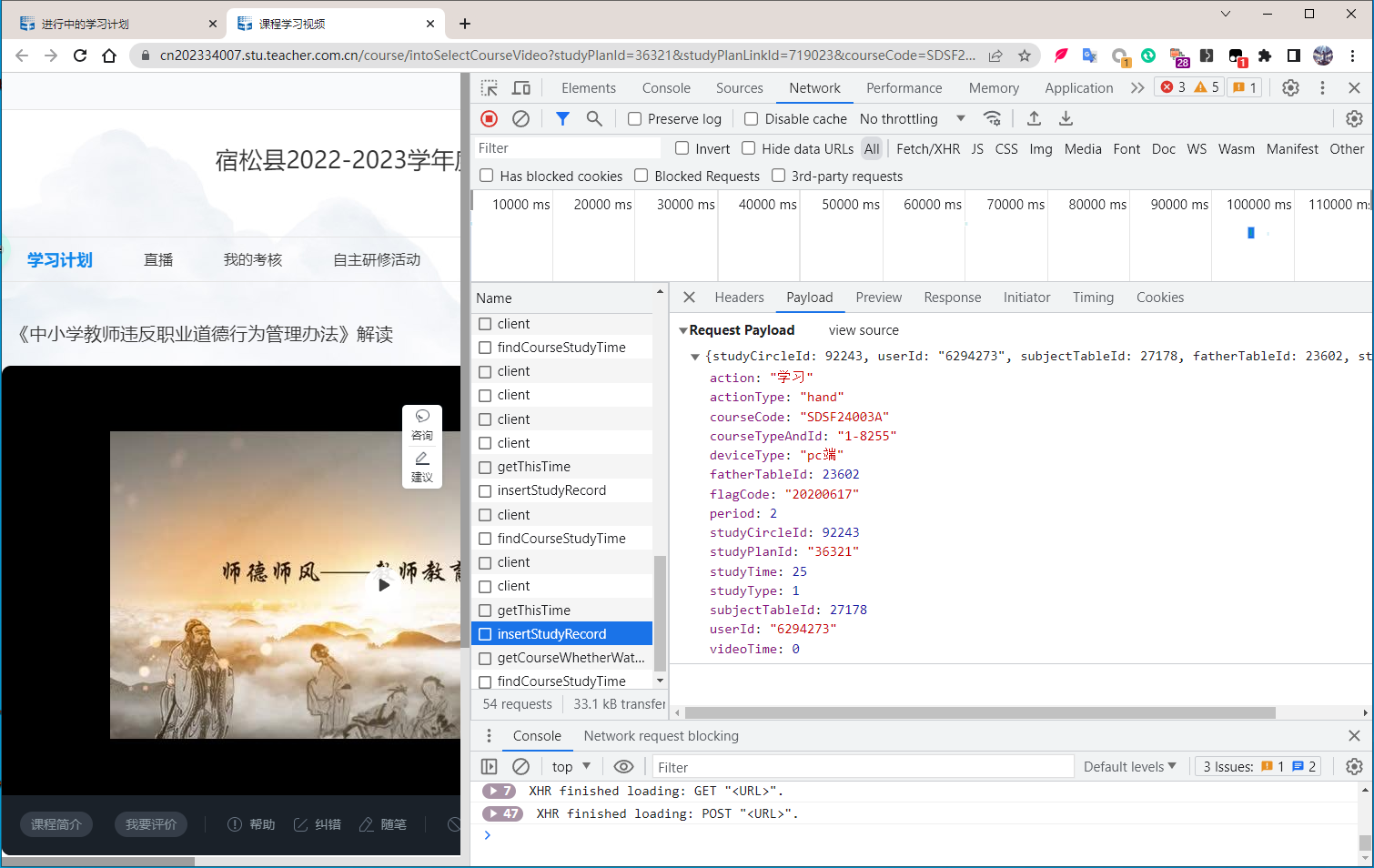
其中,insertStudyRecord使用POST方式发送了附带json数据的包给Server端,
Browser端发送的json数据包的如下:
{
"studyCircleId": 92243,
"userId": "6294273",
"subjectTableId": 27178,
"fatherTableId": 23602,
"studyType": 1,
"studyTime": 25,
"action": "学习",
"deviceType": "pc端",
"studyPlanId": "36321",
"courseCode": "SDSF24003A",
"period": 2,
"courseTypeAndId": "1-8255",
"flagCode": "20200617",
"videoTime": 0,
"actionType": "hand"
}Server端收到该POST包后的Response回复如下:
{
"isSuccess": 1
}
之后,可以看到网页中的“本课程已学习时间”增加了25分钟,因为json数据包中字段"studyTime": 25,并且Server端验证后返回了"isSuccess": 1,说明成功了,通过如下“Replay XHR”的方式再次发送该POST包,此时收到的Response如下,刷新页面后,“本课程已学习时间”并未增加,说明并没有成功增加学习时间。同时可猜测studyTime字段是否合法由Server端来判断,而并不是Server端接收到POST包后,完全信任Broswer端,进行累加学习时间。
{"data":"参数异常,计时无效_1","isSuccess":1}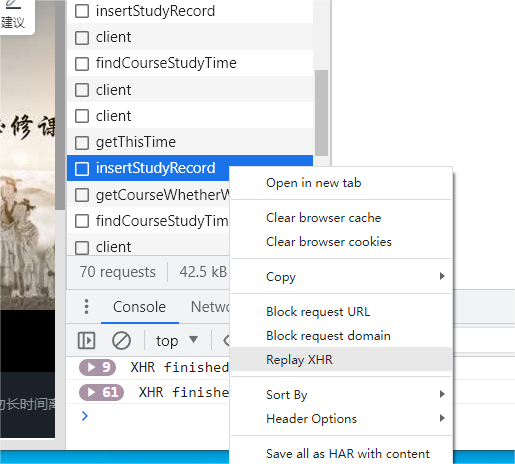
既然studyTime=25分钟无效,那么就让“studyTime=1分钟”发送insertStudyRecord包看看。经过多次测试发包总共收到以下几种Response回复。
其中累计学习时间无效的Response如下:
{"data":"参数异常,计时无效_1","isSuccess":1}{"data":"参数异常,计时无效_2","isSuccess":1}{"isSuccess":0,"msg":"操作太快了,休息一下~"}累计学习时间有效的Response只有以下一种:
{"isSuccess":1}另外还有一个findCourseStudyTime的POST包如下,
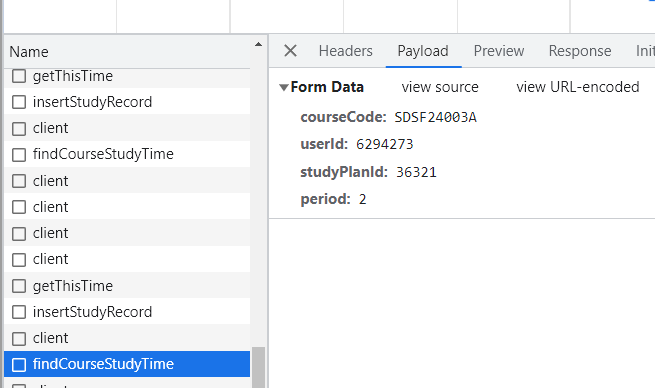
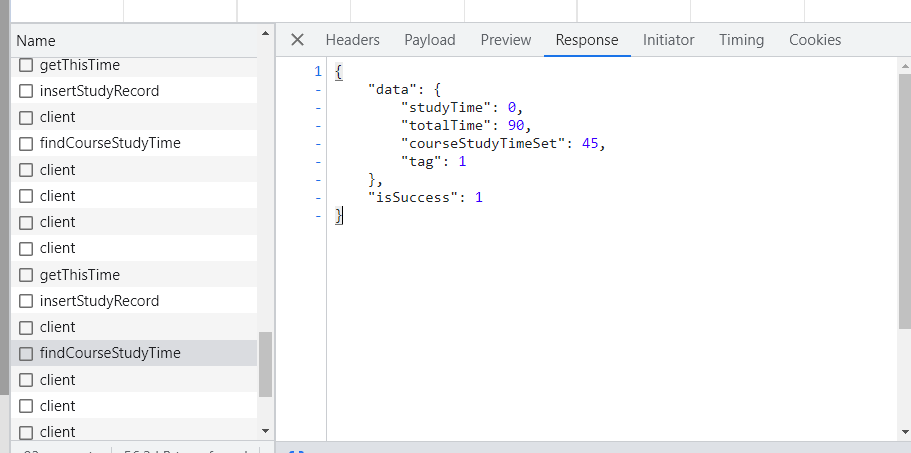
该Response的数据如下,"studyTime": 0表示“本课程已学习时间:0分钟”。在之前的实验中,发送insertStudyRecord包成功后,studyTime会随之增加。即findCourseStudyTime的POST包可以起到一个显示“课程已学习时间”的效果。
{
"data": {
"studyTime": 0,
"totalTime": 90,
"courseStudyTimeSet": 45,
"tag": 1
},
"isSuccess": 1
}
Python脚本自动化发包
那么既然insertStudyRecord包和findCourseStudyTime包可以增加学习时间和显示学习时间,那么就可以利用Python发送这两个包来刷网课了。
处理两个POST包的Python代码如下。其中每隔30s交替发送一个数据包,即每隔60s完成"studyTime": 1的1分钟学习时间的积累,cookies值可以在Network选项卡的POST包中的Headers中找到。
import requests
import time
url1 = 'https://cn202334007.stu.teacher.com.cn/studyRecord/insertStudyRecord'
url2 = 'https://cn202334007.stu.teacher.com.cn/course/findCourseStudyTime'
headers1 = {'User-Agent': ......,'Cookie': ......,"Content-Type": ......,}
headers2 = {......}
payload1 = {
"studyCircleId": 92243,
"userId": "6294273",
"subjectTableId": 27178,
"fatherTableId": 23602,
"studyType": 1,
"studyTime": 1, # 1分钟学习时间
"action": "学习",
"deviceType": "pc端",
"studyPlanId": "36321",
"courseCode": "SDSF24003A",
"period": 2,
"courseTypeAndId": "1-8255",
"flagCode": "20200617",
"videoTime": 0,
"actionType": "hand"
}
payload2 = {"courseCode":"SDSF24003A","userId":"6294273","studyPlanId":"36321","period":2}
session = requests.Session()
counter = 0
while True:
if counter % 2 == 0:
# 发送第一个POST-insertStudyRecord请求
response = session.post(url1, json=payload1, headers=headers1)
else:
# 发送第二个POST-findCourseStudyTime请求
response = session.post(url2, data=payload2, headers=headers2)
# 检查响应状态码
if response.status_code == 200:
print("请求成功")
else:
print("请求失败")
# 输出响应内容
print(response.text)
# 睡眠30秒
time.sleep(30)
# 更新计数器
counter += 1
接着处理多门课,简单分析就可以知道两个POST包中"courseCode": "SDSF24003A"代表着哪一门课,那么可以将每门课的courseCode记录下来,然后判断该门课是否学习完毕,当学习完毕后递归学习下一门课。
courseCode = ["txz099aw", "SDJX202024011A", "SDSF24002A", "SDSF24012A", "SDJX202024013A", "SDJX202024001A", "SDSF24008A", "TS202024001B", "tkc1178aw", "TS202024007A", "SDJX202024002A", "TS1924013A", "SDSF24003A", "TS202024006A", "SDJX202024012C"]其递归学习每一门课的逻辑和实现都比较简单,就不详细介绍了。最终Python代码如下:
reqs.py
import requests
import time
from study_time_finder import find_study_time
courseCode = ["txz099aw", "SDJX202024011A", "SDSF24002A", "SDSF24012A", "SDJX202024013A", "SDJX202024001A", "SDSF24008A", "TS202024001B", "tkc1178aw", "TS202024007A", "SDJX202024002A", "TS1924013A", "SDSF24003A", "TS202024006A", "SDJX202024012C"]
courseNum = 0
session = requests.Session()
while True:
# 构造请求的URL和数据
url = 'https://cn202334007.stu.teacher.com.cn/studyRecord/insertStudyRecord'
headers = {......}
post_data = {"studyCircleId":92243,"userId":"6294273","subjectTableId":22515,"fatherTableId":23581,"studyType":2,"studyTime":1,"action":"学习","deviceType":"pc端","studyPlanId":"36321","courseCode":courseCode[courseNum],"period":2,"courseTypeAndId":"2-13340","flagCode":"20200617","actionType":"hand"}
url2 = 'https://cn202334007.stu.teacher.com.cn/course/findCourseStudyTime'
headers2 = {......}
post_data2 = {"courseCode":courseCode[courseNum],"userId":"6294273","studyPlanId":"36321","period":2}
counter = 0
found = False # 表示未学满
while not found:
print("课程信息:", courseCode[courseNum])
if counter % 2 == 0:
print("*****************************************")
# ******POST-insertStudyRecord******
response = session.post(url, json=post_data, headers=headers)
# check for error code
if response.status_code == 200:
print("请求成功!", "POST-insertStudyRecord")
print("响应内容:", response.text)
else:
print("请求失败!")
print("错误码:", response.status_code)
else:
# ******POST-findCourseStudyTime******
response2 = session.post(url2, data=post_data2, headers=headers2)
# check for error codes
if response.status_code == 200:
print("请求成功!", "POST-findCourseStudyTime")
print("响应内容:", response2.text)
else:
print("请求失败!")
print("错误码:", response2.status_code)
found = find_study_time(response2.text)
print("是否学到了90分钟? ", found)
print("*****************************************\n")
time.sleep(15)
counter += 1
courseNum += 1study_time_finder.py
import json
def find_study_time(text):
data = json.loads(text) # 解析 JSON 字符串为 Python 字典
found_study_time = False # 标记是否找到目标字段
if "studyTime" in data["data"] and data["data"]["studyTime"] == 90:
found_study_time = True # 找到目标字段,设置标记为 True
return found_study_timePython测试
测试截图如下,同时用Python挂两个号刷网课。
其中的一部分输出结果如下,可以看到课程信息: TS202024001B,两个包的请求是否成功,"studyTime":41表示TS202024001B这门课已经学习了41分钟。当显示是否学到了90分钟? True的输出结果时,会自动进行下一个课程的学习。
课程信息: TS202024001B
*****************************************
请求成功! POST-insertStudyRecord
响应内容: {"isSuccess":1}
课程信息: TS202024001B
请求成功! POST-findCourseStudyTime
响应内容: {"data":{"studyTime":41,"totalTime":90,"courseStudyTimeSet":45,"updateTime":1687886780000,"tag":1,"isComplete":1},"isSuccess":1}
是否学到了90分钟? False
*****************************************彩蛋: 经过多次Python测试发现可以最小间隔30s就可以累计1分钟学习时间,即Python代码中发包时间间隔为time.sleep(15),表示15s发送一个包,30s发送完。那么也就实现了两倍速刷课!结
之前也没有调试过浏览器前端的js代码,这次阅读js代码后,发现该程序员写的注释真的详细,代码格式和命名也非常的整洁规范,这让我这位零基础的小白阅读起来基本没什么压力。其次,虽然python代码用的不熟,但是大部分代码是使用ChatGPT写的,节省了很多的时间。总之,有关于代码的问题,动手实践起来总会解决的。